Cryptography is a mathematical technique used to convert information into an unreadable form, that is, to encrypt it. Cryptology is the science of encryption with its simplest definition; deals with hiding and revealing information. The science of cryptography consists of two subsystems, cryptography and cryptanalysis.
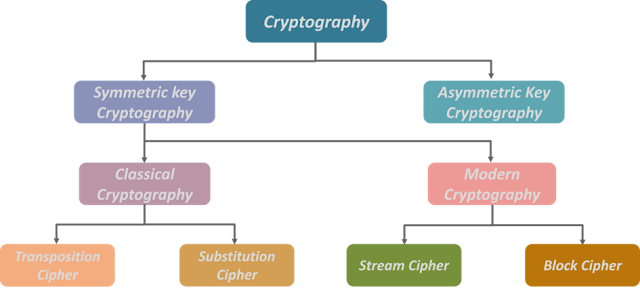
Sub-branches of cryptology
Cryptography, which takes its
name from the combination of the Greek words kryptos meaning "hidden"
and graphein meaning "writing", are mathematical techniques used to
transform information into a form that cannot be read by unwanted people, that
is, to encrypt it. People who do this are called cryptographers.
Cryptanalysis, on the other
hand, deals with the decryption of encrypted texts. People who decipher the
ciphertext and obtain the original text are called cryptanalysts.
As can be understood from
their definitions, cryptography and cryptanalysis are opposite concepts.
Therefore, throughout history, there has been a race between the people working
on these two systems. Because every new encryption algorithm developed by
cryptographers is broken by cryptanalysts forces cryptographers to design
stronger algorithms.
The protection and security
of information had an important place in ancient times as well as today. Therefore,
we can say that the history of the science of cryptography dates back to the
pre-Christian era. The hieroglyphic signs in the inscriptions found in Egypt
around 1900 BC are considered the first example of secret writing. In the years
60-50 BC, the Roman Emperor Julius Caesar was using an encryption method that
is known today as his name in state communication. This encryption method was
based on replacing each letter in a text with the third letter after it in the
alphabet.
Caesar encryption method
Let's give an example of the
Caesar encryption method using our own alphabet. In this method,
"ÖĞTJÇDÇ" was written instead of the word "HELLO".
The encryption method, which
is created by changing the places of letters, is the most primitive encryption
technique and cannot provide secure communication in the modern age. Because,
which letter in the encrypted text is replaced by a letter in the original text
can be found by comparing the most frequently used letters in that language
with the most frequently used letters in the encrypted message.
Blaise de Vigenere developed
the Vigenere system in 1586, which is similar to the Caesar cipher but more
complex. In this system, the letters in the text were not fixed, but shifted
according to a changing sequence of numbers. For example, when the encryption
number sequence or key was set as 285739, the first letter of the text to be
encrypted was shifted 2, the second letter 8, the third letter 5, ... , the
sixth letter 9 letters. If the text to be encrypted was longer than six
letters, the key was applied repeatedly. In other words, all letters of the
text, including the seventh letter of 2 and the eighth letter of 8, were
encrypted by shifting according to the key. The Vigenere cipher, which was
described as an unbreakable encryption system for a long time after it was
developed, was cracked in 1854. However, those living in the southern states in
the 1860s, when the American Civil War took place, did not yet know that this
encryption method was broken. The Northerners, who knew how to break the
Vigenere code, had a great advantage over the Southerners, who tried to
communicate using this method.
In the following years,
cryptographers all over the world struggled to develop a better encryption
method. In the Second World War, the German armies communicated among
themselves using texts encrypted with the Enigma device.
Messages encrypted with the
Enigma device were transmitted over radio waves using Morse codes. This
communication between long distances was listened and tried to be solved by the
British cryptanalysts. However, finding the key used by the Enigma device for
encryption was a very difficult and time-consuming process mathematically. At
the same time, the fact that every key used in encryption was changed every
eight hours made the job of British cryptanalysts even more difficult. An electromechanical device called Bombe,
developed by British mathematician Alan Turing and his team using a
mathematical model, was able to crack encrypted Enigma messages. This event
changed the course of the Second World War.
Until the 1950s, the science
of cryptography was only used in secure communications within states, namely in
military and diplomatic fields. However, this situation changed with the
invention of the computer and the use of the internet. Privacy is the most
important feature required for all kinds of communication and transactions we
make using the internet, which has now become an integral part of our daily
lives. Information security is provided by cryptography in many areas such as
online shopping, banking transactions, reservation systems, satellite systems,
e-government applications, e-mail messages. The most important function of
cryptography is to provide national information security. Understanding the
importance of information security and cryptography today, all countries of the
world are working for the development of new and stronger algorithms, as they
are aware that even the most reliable systems can be solved one day.


Comments
Post a Comment