Working principle
Electromagnetic signal pulses are sent, and after the
energy carried by the radio waves reaches the object, it is reflected back from
the object, these reflected signals are called echoes. The direction of echo
intensity and return time are very important for radar. In line with these
parameters, the properties of the detected object are determined.
It is also necessary for the echo reflected from the electromagnetic signal sent by the radar to be above a certain level. This level is known as the threshold value.
Areas Where Radars Are Used
Radars are used in civil and military fields. In civil use, in the fields
of air traffic control and flight management, traffic management systems, ship
traffic at sea, navigation and weather radar and search and rescue, security,
vehicles speed sensors;
Basically, we can specify the radar types as pulse radars and continuous
wave radars. Although pulse radars are the most widely used type of radar, they
work according to the basic principle we have compared above, that is, the
system logic that determines target information by sending radio waves and
using the time between reflection and reflection. They usually have a single
antenna for transmitting and receiving. After sending the wave pulses, they
wait for it to reflect from the target and return. Waves travel 300 m in 1 microsecond.
If the reflection of a wave emanating from the antenna comes after 2
microseconds, we detect that the target is 300 m away.
Continuous wave radars, on the other hand, work according to the Doppler
shift principle, although they use two different antennas for sending and
receiving, as receiver and transmitter. With this method, it can be difficult
to determine the range of a target and to distinguish between two targets.
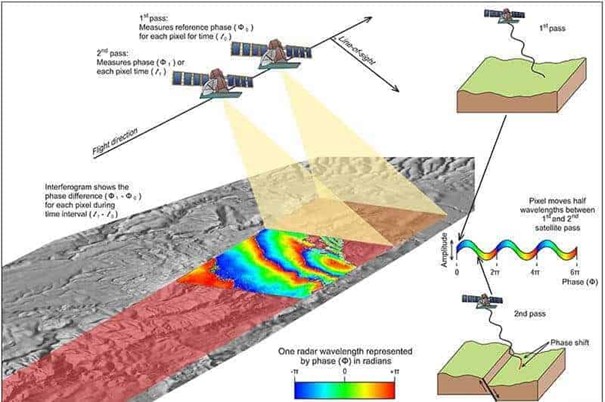
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)
It is a radar that sends waves from different and more than one point and
processes the reflected waves in accordance with the physical structure of the
world to obtain the image of the scanned area.
Resolution means a parameter to distinguish two targets that are close to
each other. There are two different resolution variants. Azimuth and range
resolution. Azimuth is the effect of detecting two targets as a single target
when they are equidistant and close to each other with respect to the radar's
antenna. On the other hand, when two targets are at the same distance from the
radar station, if one of the waves of the two targets arrives before the other,
the radar detects it as a single target.
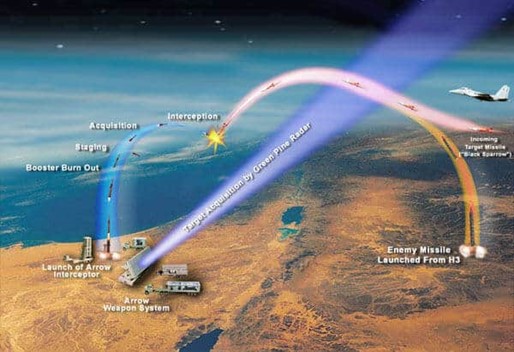
Arthur Radar, this radar with passive phased array antenna can detect the
trajectory of a missile with high precision. Its antenna can scan both
elevation and azimuth angles. It can detect dozens of targets simultaneously.
GreenPine Radar
This radar has a phased array antenna and its signals are located in the C
band in the frequency range of 500 MHz to 1000 MHz. It can scan an average
range of 500 km.
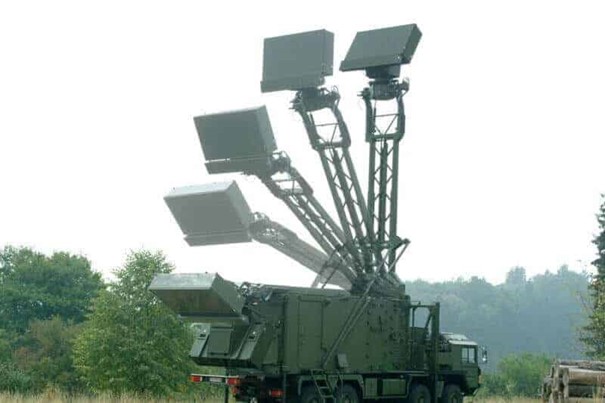
TRML-3D 3-dimensional radar
It can detect different types of targets and detect
the variable parameters of these targets and classify these vehicles.
Meteor 500 Doppler Radar
Weather
analysis and instant weather forecasts can be made with high resolution data.







Comments
Post a Comment