Generators, which are frequently used in hospitals, schools and workplaces, are the most ideal machines to ensure the continuity of electrical energy systems. The first generator was made by physicist Michael Faraday in 1831 and has managed to develop and diversify until today. Working principle of generators; is the conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy. In short, it is a kind of electrical energy generator that can convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
What Does a Generator Do?
If there is no
electrical energy due to network failures or at the address of residence,
electrical energy can be produced through generators. As soon as the electrical
current from the network is cut off, it can serve as electrical energy for
workplaces, houses or the whole building, thanks to the generators that run
automatically after 10 seconds.
How Does the Generator Work?
Each generator has one alternator. In addition, there is an engine. According
to the type, converted fuels such as gasoline – natural gas are located in the
engine area of the generators. This fuel is primarily converted into heat
energy. It is then converted into mechanical energy form to provide electrical
energy. Finally, the mechanical energy form obtained is sent to the alternator
located directly on the engine. The alternator part starts to become magnetized
with the transformation of the mechanical effect and reaches the result, that
is, electrical energy is obtained.
In order to
obtain electrical energy, the rotation effect needs to be realized and this
must be converted into magnetization energy in the next step. Technically, this
is how electrical energy is produced, from power plants to our cars. For
example, our fuel in our cars is first sent to the engine and then to the
alternator, where the engine turns. After that, it appears as electrical
energy.
Where is the generator used?
Where is the
generator used? Generators with a very wide usage area; It can be preferred in
many areas from houses to workplaces, from factories to buildings under public
administration, from industrial buildings to apartments. In addition, it can be
used in areas where electricity is not available or not.
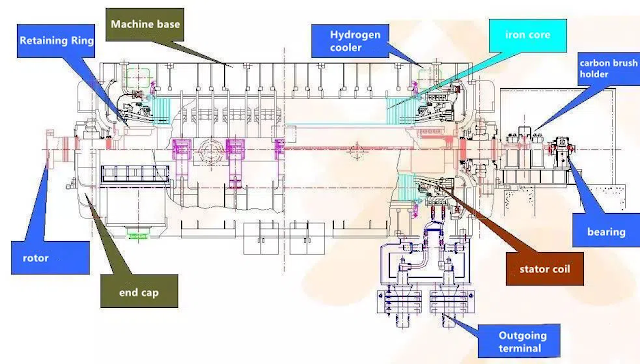
What are the Main Parts of Generators?
The parts of
the generator are as follows;
·
Engine
It is the part
that allows fuels such as gasoline to be burned. It converts into heat energy
by burning, and heat energy is converted into mechanical energy. The larger the
engine displacement – the greater the capacity to generate electricity will be.
·
Alternator
It is the area
where the electrical energy is obtained. The mechanical energy form is
converted into electrical energy by the alternator.
·
Control Panel
It is the
electrical-electronic control area where the generator, which is the
alternative electricity generation equipment, is adjusted after how many
seconds it will operate when the electrical current from the mains is cut off.
·
Chassis – Fuel Tank
The area that
ensures that the generators do not move from its place during operation is
called the chassis. Chassis is also preferred as a kind of reservoir where fuel
is put. While there are generators with the fuel tank located on the chassis,
there are also generator types located outside the chassis.
·
Radiator
The radiator,
which is among the generator elements, is a propeller system that prevents
excessive increase in temperature by providing cooling of the hot engine.
·
Cabin
If the
generator to be used is to be left outside, it is controlled with a comfortable
cabin both to protect it from environmental effects and to make less noise. Here,
we also answer the question of what is a cabin generator.
·
Lubrication System
It is very
important to lubricate the generator engine at certain intervals. For this
reason, a kind of reservoir is located in each generator, including an oil pump
for the lubrication system.
·
Exhaust System
Some
generators have internal combustion engine technology. Therefore, continuous
exhaust gas output is made. These gases are not only dangerous for human
health, but also affect the life and operation of the generator. For this
reason, it is necessary to keep it away from both the engine and human
breathing. The areas that are slightly removed from the engine in a kind of
tubular form are called the exhaust system.
Starter and Battery System
There is a starter, that is, electrical equipment that allows the generator
to be manually controlled. It has its own battery. In addition, it does not
need to be charged. Thus, we explain the question of what is a starter
generator, which is one of the most frequently asked questions.
Generator Types According to Fuel Types
There are 4
different types of generators. These;
·
Generators producing electrical energy with diesel fuels
·
Generators that obtain electrical energy by consuming gasoline
·
Generators that can produce electrical energy with natural gas combination
·
Generators used to provide electrical energy with LPG systems
Generator Types According to Usage Target
Purpose 1: Continuously Producing Electricity
It can be preferred to provide continuous load, that is, to provide
continuous energy production. It is generally used in construction sites or
mines and shipping areas where there are difficulties – security vulnerabilities
for the transmission or sequencing of energy. Except for these sections, this
type of generator is used wherever there is demand.
Purpose 2: Use
as Backup Energy
It can be preferred as backup energy only if the current from the mains is
interrupted in places where there is network distribution.
Purpose 3:
Mobile – Mobile Energy Source
There are also
generators developed on wheels. With such vehicles, the electricity demand
arising from mountain - hill - forest, in short, the electricity network cannot
be transmitted and mobile works are provided. It can be moved from one place to
another by connecting to the back of a powerful road vehicle such as off-road
vehicles, tractors, trucks. Compared to other generators, their power capacity
is lower.
Purpose 4: As
a Portable Power Source
It is one of
the generators with air cooling systems. They are generally preferred in areas
such as gardens and have powers between 10 and 12 kV. They are easy to carry
and do not have heavy volume and weight.
What is Prime
– Standby – Continuous? What Does It Do?
The following
options are available in all types of generators. The request is tailored to
the need;
·
What is Standby Power? What Does It Do?
They serve for
limited times. They are used as backup energizers only in cases where the mains
currents are not available. These are generator types that cannot be
overloaded. They can provide an average of 200 hours of service in 365 days.
·
What is Prime Power? What Does It Do?
These are
generators that are suitable for 10% overload loading every 12 hours. They can
offer the opportunity to work at variable loads.
·
What is Continuous Power? What Does It Do?
They can only be used
when fixed loads are required. It does not offer the possibility of
overloading. In such power options, the average load level can be 100%.
Comments
Post a Comment